Our Services
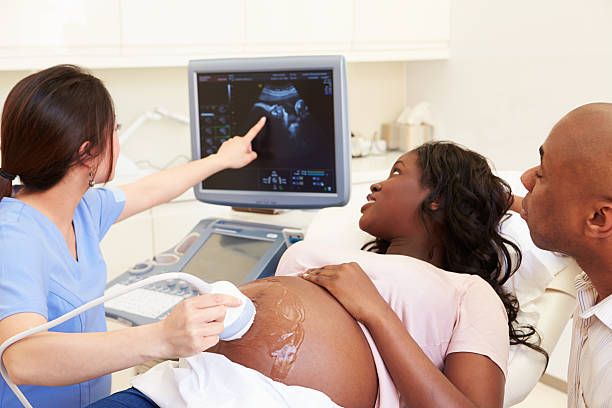
Ultrasonography(USG)
It is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of internal organs, tissues, and blood vessels. A transducer sends sound waves into the body, which reflect off internal structures and return as echoes. They are Abdomen, Abdominal & Pelvis, Pelvis, Chest, Follicular Study
How it works
- The transducer sends sound waves into the body.
- These waves bounce back from the different tissues and organs.
- The reflected sound waves are picked up by the transducer, which sends them to a computer.
- The computer converts the sound wave data into an image that can be viewed on a monitor.
- Unlike X-rays, ultrasound does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer option.
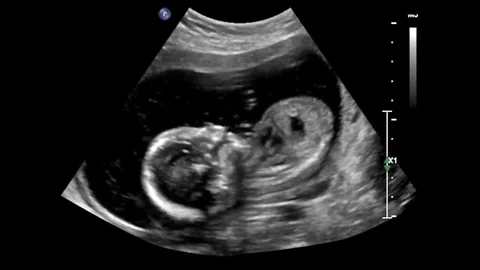
Obstetric USG
It is a safe, non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to create real-time images of a developing fetus in the uterus. It is used to confirm pregnancy, monitor fetal growth and development, determine gestational age, check for multiple pregnancies, and screen for abnormalities or birth defects. They are First Trimester Scan / Early Viability, Routine Obstetric USG (Growth Scan), NT Scan (11–14 weeks), Anomaly Scan (18–20 weeks), Obstetric Doppler
Safety and benefits
- The procedure is painless, non-invasive, and does not use ionizing radiation like X-rays.
- There are no known harmful effects on the mother or baby from diagnostic ultrasound use.
- It allows for early detection of potential complications, enabling timely treatment.
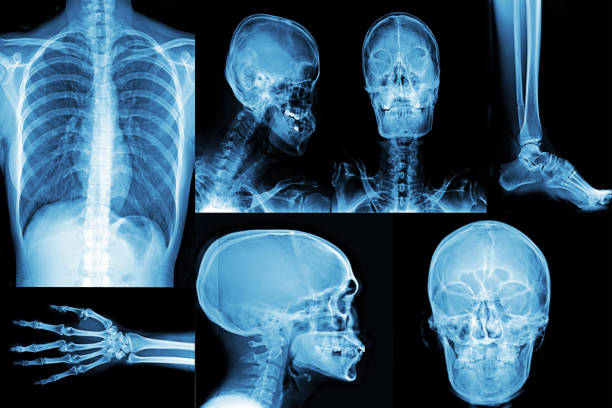
Digital X-Ray
Digital X-rays are an advanced form of medical imaging that uses digital sensors instead of traditional photographic film to produce and store images of the body’s internal structures. This technology offers several significant advantages over traditional X-rays, including higher image quality, lower radiation exposure, and faster results. They are Chest, PA / AP, PNS (Water’s View), Cervical Spine, Thoracic Spine, TL Spine, Lumbar Spine, Abdomen Erect,KUB and Others.
How it works
- An x-ray source sends a beam of radiation through the body, just like a traditional x-ray.
- Instead of film, a digital detector captures the x-rays.
- The detector converts the x-rays into an electronic signal, which is sent to a computer.
- The computer processes this signal to create a high-resolution digital image that is displayed on a screen within seconds.
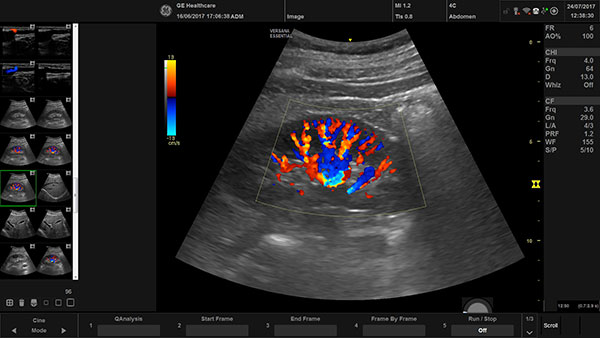
High Resolution (USG)
It is an advanced imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create detailed, non-invasive images of superficial soft tissues. It is particularly useful for evaluating peripheral nerves, skin lesions, and other superficial structures, and is used to diagnose conditions like peripheral neuropathies, skin cancers, and nerve injuries from trauma or surgery. They are Neck / Thyroid, Neuro Sonography, Breast, Eye & Orbits, Scrotum, Soft Tissue.
How it works
- Frequency and resolution: A higher frequency results in a narrower sound beam, which leads to better resolution and more detailed images.
- Contrast enhancement: Techniques like Quantitative High-Definition Microvasculature Imaging (HDMI) can visualize very small vessels.
- Elastography: This technique can be used to assess the stiffness of tissue, which helps differentiate between benign and malignant tumors.

Special Procedures
“Special Procedures” most commonly refers to a series of mechanisms established by the UN Human Rights Council, which includes independent experts with mandates to report and advise on specific human rights issues from a thematic or country-specific perspective. These experts, known as Special Rapporteurs or Independent Experts. They are Barium Studies, HSG (Hysterosalpingography), RGU, IVP (Intravenous Pyelogram). These experts monitor human rights, respond to violations, and provide guidance to governments through activities like country visits and communications, and they serve in their personal capacity for a limited time without pay.